|
|
| Weather forecasting process | Natural disasters and measures | Learn about weather |
Natural disasters and measures
Report about the observation and information on earthquake and tsunami
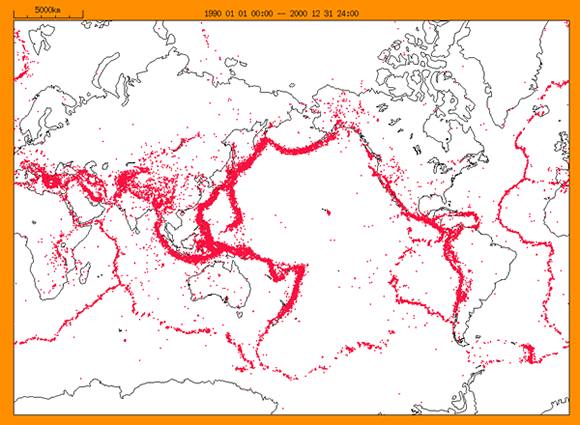
Japan has more earthquakes than any other countries. About 10 percent of all the earthquakes in the world occur in Japan. Big earthquakes like the Great Hanshin Earthquake can destroy buildings and kill people.
Earthquakes can also cause tsunami, large ocean waves. Since Japan is surrounded by sea, tsunami can sweep over cities and people on the land just like the Southwest-off Hokkaido Earthquake.
Observations of earthquake and tsunami are made for 24 hours a day to protect us and prevent or reduce damage. When an earthquake occurs, its information of earthquake and tsunami is reported immediately through city halls, government offices and television.
An earthquake or tsunami occurs outside of Japan too. Tsunami occurred offshore of the pacific coast of South America can reach Japan. The countries all around the world work together and share earthquake data and tsunami information.
Photographs supplied courtesy of Japan Meteorological Agency
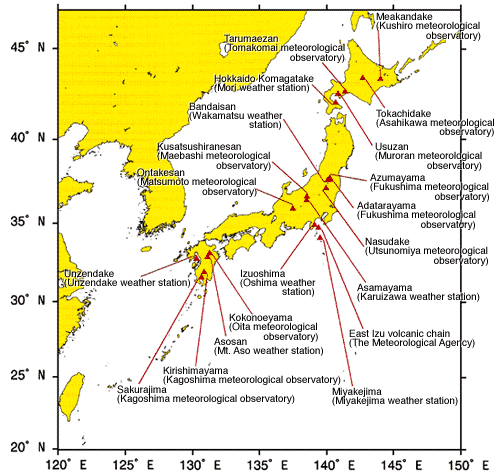
Observing volcanoes and announcing the information
Volcano with eruption or fumarolic activity is called active volcano. It s said that there are about 1,500 active volcanoes in the world.
Japan has 108 active volcanoes and it is about ten percent of the worldfs active volcanoes. Although they repeat eruption, many people in Japan live near active volcanoes and even some area become tourist spots for hot springs. Observation stations keep a twenty-four-a-day watch on volcanoes to protect lives and prevent/reduce damage. Volcanic activity is quickly reported by radio, television and so on.
Photographs supplied courtesy of Japan Meteorological Agency
Can earthquakes be predicted?
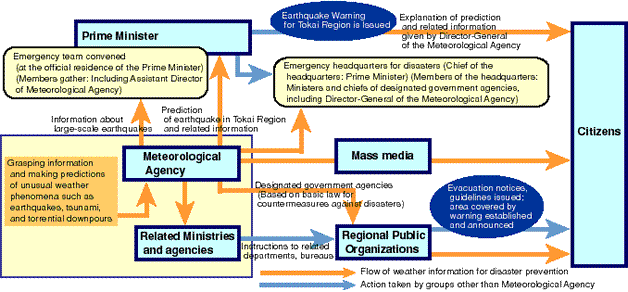
It is very difficult to predict exactly when and where earthquakes will occur and to tell how big they will be. However, Japanese scientists think it may be possible to predict Tokai earthquake (about 8-magnitude earthquake in Tokai zone and around the area of the west coast in the Suruga Bay). Therefore, they set observation and detection devices in this area and they observe it for 24 hours. If anything unusual is detected and they analyze it as sign of an earthquake, the head of the Meteorological Agency will report the Prime Minister. The Prime Minister will announce the warning to the public.
Copyright© 2007-2011 Japan Transport Promotion Association. All rights reserved.
|